Maximizing the efficiency of multienzyme process by stoichiometry optimization
Abstract
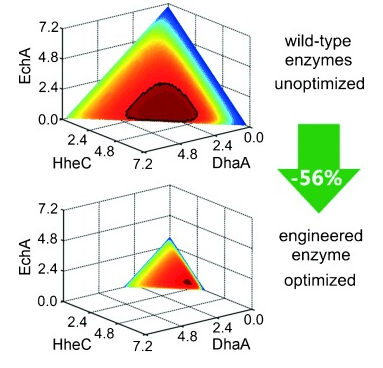
Multienzyme processes represent an important area of biocatalysis. Their efficiency can be enhanced by optimization of the stoichiometry of the biocatalysts. Here we present a workflow for maximizing the efficiency of a three‐enzyme system catalyzing a five‐step chemical conversion. Kinetic models of pathways with wild‐type or engineered enzymes were built, and the enzyme stoichiometry of each pathway was optimized. Mathematical modeling and one‐pot multienzyme experiments provided detailed insights into pathway dynamics, enabled the selection of a suitable engineered enzyme, and afforded high efficiency while minimizing biocatalyst loadings. Optimizing the stoichiometry in a pathway with an engineered enzyme reduced the total biocatalyst load by an impressive 56 %. Our new workflow represents a broadly applicable strategy for optimizing multienzyme processes.